Geolocation vs Geofencing: The Complete Guide to Location-Based Technologies
Understanding the fundamental differences, applications, and choosing the right solution for your business in
Table of Contents
Introduction to Location Technologies
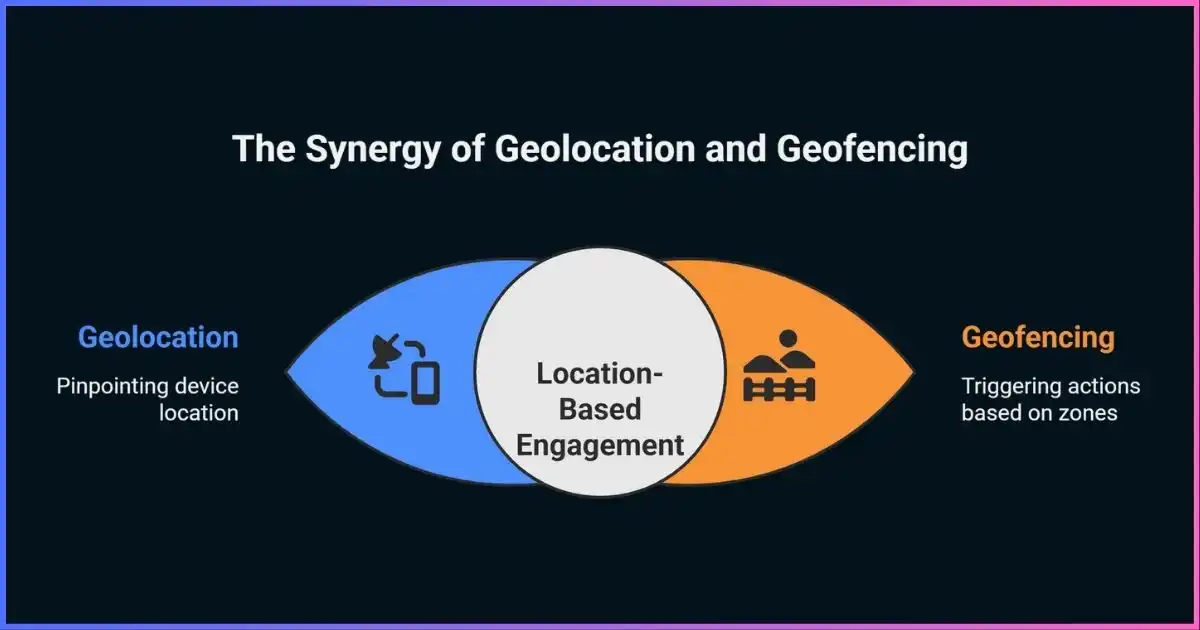
In today’s digital landscape, location-based technologies have become fundamental to countless applications, from ride-sharing services to targeted marketing campaigns. When discussing location technologies, two terms frequently emerge in conversation: geolocation and geofencing. While these technologies are often used interchangeably, they serve distinctly different purposes and offer unique capabilities for businesses and developers.
Understanding the difference between geolocation vs geofencing is crucial for making informed decisions about which technology best suits your specific needs. Geolocation focuses on determining and tracking the precise position of a device or user, while geofencing creates virtual boundaries that trigger actions when crossed. Both technologies have revolutionized how businesses interact with customers, optimize operations, and deliver personalized experiences.
This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamental differences between geolocation and geofencing, examine their respective strengths and limitations, analyze market trends with current statistics, and provide practical guidance for choosing the right solution. Whether you’re a business owner looking to implement location-based marketing, a developer building the next great app, or simply curious about these technologies, this article will provide you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions.
What You’ll Learn
- The fundamental differences between geolocation and geofencing technologies
- Current market statistics and adoption trends for 2024
- Practical applications and use cases for each technology
- Implementation costs and ROI considerations
- Step-by-step guidance for choosing the right solution
Ready to Implement Location Technology?
Get started with professional geo-targeting solutions that drive real results
Explore Geo Targetly Solutions →What is Geolocation?
Geolocation is the process of identifying and determining the real-world geographic location of an internet-connected device, such as a smartphone, tablet, or computer. This technology uses various methods to pinpoint a device’s position, including GPS satellites, cellular tower triangulation, Wi-Fi positioning, and IP address mapping.
How Geolocation Works
Primary Methods:
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Uses satellite signals to determine precise coordinates, accurate within 3-5 meters
- Cellular Triangulation: Calculates position based on signal strength from multiple cell towers
- Wi-Fi Positioning: Uses known Wi-Fi hotspot locations to estimate device position
- IP Geolocation: Determines approximate location based on internet service provider data
Key Characteristics:
- Continuous Tracking: Real-time location updates
- High Accuracy: Precise coordinate data
- Global Reach: Works anywhere with signal coverage
- Device-Centric: Focuses on individual device locations
Geolocation Accuracy Comparison
Common Geolocation Applications
Navigation & Maps
Turn-by-turn directions, traffic updates
Delivery Tracking
Real-time package and fleet monitoring
Emergency Services
911 location services, disaster response
What is Geofencing?
Geofencing is a location-based service that creates virtual boundaries around real-world geographic areas. When a GPS-enabled device enters or exits these predefined virtual perimeters, the geofence triggers predetermined actions such as sending notifications, logging data, or activating specific application features.
How Geofencing Works
Setup Process:
- Define Virtual Boundaries: Create circular or polygonal zones around specific locations
- Set Trigger Conditions: Specify entry, exit, or dwell time parameters
- Configure Actions: Program responses like notifications, data collection, or API calls
- Monitor Events: Track when devices cross boundaries and execute actions
Geofence Types:
- Circular Geofences: Radius-based boundaries around points of interest
- Polygonal Geofences: Custom-shaped boundaries following property lines
- Static Geofences: Fixed locations like stores or offices
- Dynamic Geofences: Moving boundaries around vehicles or people
Geofencing Market Adoption by Industry
Geofencing Trigger Events
Entry Events
Triggered when device enters geofence
Exit Events
Activated when device leaves geofence
Dwell Events
Triggered after specified time in zone
Key Differences Between Geolocation and Geofencing
While both geolocation and geofencing rely on location data, they serve fundamentally different purposes and operate through distinct mechanisms. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate technology for your specific use case.
| Aspect | Geolocation | Geofencing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Determine and track precise location coordinates | Create virtual boundaries and trigger actions |
| Data Type | Continuous coordinate streams (lat/long) | Event-based boundary crossings |
| Battery Impact | High (continuous GPS usage) | Low to moderate (periodic location checks) |
| Accuracy Requirements | High precision (1-5 meters) | Moderate precision (10-100 meters) |
| Real-time Processing | Continuous location updates | Event-triggered responses |
| Privacy Concerns | Higher (detailed movement tracking) | Lower (zone-based notifications only) |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Cost Structure | Based on API calls and data volume | Based on geofence quantity and events |
Technology Usage Comparison
When to Choose Geolocation
- Need precise, real-time location tracking
- Building navigation or mapping applications
- Fleet management and asset tracking
- Emergency response systems
- Location-based analytics and insights
When to Choose Geofencing
- Location-based marketing campaigns
- Automated attendance tracking
- Security and access control
- Customer engagement at retail locations
- IoT device automation
Ready to Implement Location Technology?
Get started with professional geo-targeting solutions that drive real results
Explore Geo Targetly Solutions →Market Statistics and Trends
The location-based services market continues to experience robust growth, driven by increasing smartphone adoption, IoT proliferation, and growing demand for personalized experiences. Current market data reveals significant opportunities for businesses implementing both geolocation and geofencing technologies.
$24.3B
Global LBS Market Size 2025
3.8B
Active LBS Users Worldwide
26.8%
Expected CAGR 2025-2029
Market Size Projection: Geolocation vs Geofencing
Key Market Insights
Growth Drivers
- Mobile Device Penetration: 6.8 billion smartphone users globally
- 5G Network Rollout: Enhanced location accuracy and reduced latency
- IoT Expansion: 29 billion connected devices expected by 2030
- Privacy Regulations: Driving demand for compliant solutions
Industry Applications
- Retail & E-commerce: 32% of market share
- Transportation & Logistics: 28% of market share
- Healthcare: 15% of market share
- Government & Defense: 12% of market share
Regional Market Distribution
Technology Comparison: Performance Metrics
Understanding the technical performance characteristics of geolocation vs geofencing is essential for making informed implementation decisions. This section provides detailed comparisons of accuracy, battery consumption, response times, and other critical metrics.
Accuracy vs Battery Consumption Analysis
Geolocation Technical Specs
Geofencing Technical Specs
Platform-Specific Considerations
iOS Platform
- • Core Location framework provides both services
- • Significant location change API for battery optimization
- • Background app refresh limitations
- • Maximum 20 monitored regions per app
- • Requires location permission prompts
Android Platform
- • Google Play Services Location API
- • Doze mode and app standby optimizations
- • Background location restrictions (Android 10+)
- • Up to 100 monitored geofences per app
- • Granular permission controls
Ready to Implement Location Technology?
Get started with professional geo-targeting solutions that drive real results
Explore Geo Targetly Solutions →Business Applications and Use Cases
Both geolocation and geofencing technologies offer compelling business applications across various industries. Understanding these real-world use cases helps demonstrate the practical value and ROI potential of implementing location-based solutions.
Retail and E-commerce
Geolocation Applications:
- • Store Locators: Help customers find nearby locations with real-time inventory
- • Delivery Optimization: Route planning and real-time tracking for last-mile delivery
- • Location Analytics: Customer movement patterns and foot traffic analysis
- • Dynamic Pricing: Location-based pricing strategies and promotions
Geofencing Applications:
- • Proximity Marketing: Send targeted offers when customers approach stores
- • Customer Engagement: Welcome messages and loyalty program notifications
- • Competitor Analysis: Track visits to competitor locations
- • Event-Based Promotions: Stadium and venue-specific campaigns
Transportation and Logistics
Geolocation Applications:
- • Fleet Management: Real-time vehicle tracking and route optimization
- • Asset Tracking: Monitor valuable cargo and equipment location
- • Driver Behavior: Speed monitoring, harsh braking, and safety analytics
- • Fuel Management: Optimize routes to reduce fuel consumption
Geofencing Applications:
- • Delivery Notifications: Automatic customer alerts when packages arrive
- • Warehouse Automation: Trigger actions when vehicles enter/exit facilities
- • Driver Time Tracking: Automated attendance and job site verification
- • Security Alerts: Notifications for unauthorized vehicle movement
Healthcare and Safety
Geolocation Applications:
- • Emergency Response: Precise location for ambulance dispatch and 911 services
- • Patient Tracking: Monitor elderly or dementia patients for safety
- • Medical Asset Tracking: Locate critical equipment in hospitals
- • Contact Tracing: Track disease exposure and movement patterns
Geofencing Applications:
- • Patient Safety: Alerts when patients leave designated safe areas
- • Medication Reminders: Location-based prescription notifications
- • Staff Management: Automated check-ins for healthcare workers
- • Quarantine Monitoring: Ensure compliance with isolation requirements
Industry ROI Comparison
Implementation Costs and Pricing Models
Understanding the cost structure of geolocation vs geofencing implementations is crucial for budget planning and ROI calculations. Costs vary significantly based on accuracy requirements, usage volume, and feature complexity.
Cost Breakdown by Implementation Scale
Geolocation Pricing Models
Basic GPS Tracking
$0.001 – $0.005 per API call
Standard accuracy, basic features
High-Precision Tracking
$0.01 – $0.05 per API call
Sub-meter accuracy, real-time updates
Enterprise Solutions
$500 – $5,000+ per month
Custom features, dedicated support
Additional Costs
- • Development: $10,000 – $100,000
- • Hardware (if required): $50 – $500 per device
- • Maintenance: 15-20% of development cost annually
Geofencing Pricing Models
Basic Geofencing
$0.10 – $0.50 per geofence per month
Standard boundaries, basic triggers
Advanced Features
$1.00 – $5.00 per geofence per month
Custom shapes, multiple triggers, analytics
Enterprise Platforms
$200 – $2,000+ per month
Unlimited geofences, white-label options
Additional Costs
- • Development: $5,000 – $50,000
- • Integration: $2,000 – $20,000
- • Support: 10-15% of platform cost annually
Cost Optimization Strategies
For Geolocation:
- • Use appropriate accuracy levels for your use case
- • Implement smart location caching to reduce API calls
- • Batch location requests when real-time isn’t critical
- • Consider hybrid approaches combining GPS and cellular
- • Negotiate volume discounts for high-usage applications
For Geofencing:
- • Start with fewer, larger geofences and refine over time
- • Use dynamic geofences to reduce total count
- • Implement client-side processing where possible
- • Choose platforms with transparent pricing models
- • Monitor and optimize trigger frequency
Need Expert Guidance on Location Technology?
Professional implementation services and ongoing support available
Get Professional Consultation →Choosing the Right Solution: Decision Framework
Selecting between geolocation and geofencing requires careful consideration of your specific requirements, budget constraints, and long-term objectives. This decision framework will guide you through the evaluation process systematically.
Decision Matrix
| Evaluation Criteria | Weight | Geolocation Score | Geofencing Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Requirements | High | 9/10 | 6/10 |
| Battery Efficiency | High | 4/10 | 8/10 |
| Implementation Complexity | Medium | 6/10 | 8/10 |
| Cost Effectiveness | High | 5/10 | 8/10 |
| Real-time Capabilities | Medium | 9/10 | 7/10 |
| Privacy Compliance | High | 6/10 | 8/10 |
Choose Geolocation If:
- You need precise, continuous location data
- Building navigation or tracking applications
- Real-time updates are critical
- You have budget for higher operational costs
- Users expect precise location features
Choose Geofencing If:
- Location-based notifications are primary goal
- Battery life is a major concern
- Event-driven actions are sufficient
- Cost optimization is priority
- Privacy concerns are significant
Hybrid Approach If:
- You need both precise tracking and boundary alerts
- Different features require different approaches
- You want to optimize for different user scenarios
- Budget allows for comprehensive solution
- Long-term scalability is important
Implementation Roadmap
Requirements Analysis (Week 1-2)
Define use cases, accuracy needs, budget constraints, and success metrics
Technology Selection (Week 3)
Choose platform, evaluate vendors, and create technical specifications
Proof of Concept (Week 4-6)
Build minimal viable product, test core functionality, and validate approach
Development & Testing (Week 7-12)
Full implementation, quality assurance, and performance optimization
Deployment & Monitoring (Week 13+)
Production rollout, user training, and ongoing performance monitoring
Frequently Asked Questions
The main difference lies in their primary function: geolocation determines and tracks the precise coordinates of a device or user, providing continuous location data. Geofencing, on the other hand, creates virtual boundaries around specific areas and triggers actions when those boundaries are crossed. Geolocation is about “where,” while geofencing is about “when you enter or leave where.”
Geofencing is generally more battery-efficient than continuous geolocation tracking. Geofencing uses periodic location checks rather than constant GPS monitoring, which can reduce battery consumption by 60-80%. However, the actual battery impact depends on factors like update frequency, accuracy requirements, and platform optimizations.
Yes, many successful applications use both technologies strategically. For example, a delivery app might use geolocation for real-time driver tracking and route optimization, while using geofencing to automatically notify customers when the driver approaches their location. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of both technologies.
Geolocation typically has higher privacy implications because it continuously tracks precise location data, creating detailed movement patterns. Geofencing is more privacy-friendly as it only triggers events when boundaries are crossed, without storing continuous location history. Both require explicit user consent and should comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Geofencing accuracy typically ranges from 10-100 meters, depending on the location method used and environmental factors. GPS-based geofences are most accurate (10-30 meters), while cellular-based ones can have wider margins (50-300 meters). Urban areas with tall buildings may experience reduced accuracy due to GPS signal reflection.
Key cost factors include: accuracy requirements (higher precision costs more), usage volume (more API calls or events), platform complexity, integration requirements, ongoing maintenance, and whether you build custom solutions or use existing platforms. Enterprise features like analytics, white-labeling, and dedicated support also increase costs.
iOS limits apps to monitoring 20 geofences simultaneously, while Android allows up to 100. Both platforms have background processing restrictions that can affect real-time capabilities. iOS requires more explicit user permissions, while Android has granular location permission controls. These limitations must be considered during the design phase.
ROI varies significantly by industry and implementation. Retail businesses typically see 15-25% increases in foot traffic and sales conversion. Logistics companies report 20-30% operational cost reductions. Healthcare facilities experience 35% fewer safety incidents. The key is setting clear metrics and measuring improvements systematically.
Transform Your Business with Location Intelligence
Join thousands of businesses already leveraging location-based technologies for growth
Conclusion
The choice between geolocation vs geofencing ultimately depends on your specific business requirements, technical constraints, and strategic objectives. Both technologies offer unique advantages and serve different purposes in the location-based services ecosystem.
Geolocation excels in scenarios requiring precise, continuous location tracking, making it ideal for navigation applications, fleet management, and real-time asset monitoring. Its strength lies in providing detailed coordinate data that enables sophisticated analytics and precise user experiences. However, this capability comes with higher battery consumption, increased privacy concerns, and greater implementation complexity.
Geofencing, conversely, shines in applications focused on location-based automation and user engagement. Its event-driven nature makes it perfect for proximity marketing, automated check-ins, and boundary-based notifications. The technology offers better battery efficiency, simpler implementation, and more privacy-friendly operation, though with less precision and limited real-time capabilities.
The most successful implementations often combine both technologies strategically, leveraging geolocation for core tracking functionality while using geofencing for user engagement and automated responses. This hybrid approach maximizes the benefits of each technology while mitigating their individual limitations.
As location-based services continue to evolve with emerging technologies like 5G, edge computing, and improved privacy frameworks, the opportunities for innovative applications will expand. The key to success lies in understanding your users’ needs, respecting their privacy, and choosing the right technology stack to deliver value efficiently and effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Technology Choice Matters: Select based on precision needs, battery constraints, and use case requirements
- Hybrid Approaches Work: Combining technologies often provides the best user experience and business value
- Privacy is Paramount: Implement transparent consent mechanisms and data minimization practices
- ROI is Measurable: Track specific metrics to validate technology investments and optimize performance
- Platform Considerations: Account for iOS and Android limitations during planning and development
Disclosure: We may earn commission for purchases that are made by visitors on this site at no additional cost on your end. All information is for educational purposes and is not intended for financial advice. Read our affiliate disclosure.