IP Geolocation Databases: The Complete Guide for
Understanding the technology that powers location-based intelligence in the digital world
IP geolocation databases have become an essential technology for businesses seeking to harness location-based intelligence in today’s digital landscape. These powerful tools map IP addresses to physical locations, providing valuable insights that drive personalization, security, and business intelligence. With the global IP geolocation market projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2033, understanding this technology is more important than ever for businesses across all sectors.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about IP geolocation databases in – from how they work and their technical limitations to implementation methods and real-world applications. We’ll examine the leading providers, compare their features and pricing, and help you make informed decisions about integrating this technology into your business strategy.
What Are IP Geolocation Databases?
IP geolocation databases are specialized repositories of information that map Internet Protocol (IP) addresses to their corresponding physical locations. These databases contain millions of records that associate IP addresses with geographical data such as country, region, city, postal code, latitude, longitude, and often additional metadata like ISP information, connection type, and timezone.
At their core, these databases serve as the backbone for various location-based services and technologies that need to determine where online users or devices are physically located without requiring explicit permission or GPS data. They transform the anonymous numeric IP addresses that identify devices on the internet into actionable location intelligence.
The data in these databases is compiled through various methods, including:
- Analysis of IP address allocation records
- Network routing information
- User-supplied location data
- Wi-Fi positioning data
- Proprietary algorithms and triangulation methods
- Partnerships with ISPs and network operators
These databases are continuously updated to reflect changes in IP address assignments, as network topologies evolve and ISPs reallocate address blocks. Most reputable providers update their databases daily or weekly to maintain accuracy.
How IP Geolocation Databases Work
IP geolocation databases operate on the principle that IP addresses are allocated to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) in geographically organized blocks. While IP addresses themselves don’t inherently contain location information, their assignment patterns provide clues about physical locations.
The Technical Process
When you look up an IP address in a geolocation database, here’s what happens behind the scenes:
- IP Address Lookup: The system takes the target IP address and queries the database.
- Database Matching: The database identifies which IP range or block contains the address.
- Location Retrieval: Once matched, the system returns the associated geographical information.
- Additional Data Association: Many databases also provide supplementary information like ISP name, connection type, and organization.
Most commercial databases use sophisticated algorithms that incorporate multiple data sources to improve accuracy. Some providers employ techniques like:
- Network Latency Analysis: Measuring response times between the IP address and various points with known locations
- Hostname Analysis: Examining DNS naming conventions that may contain location hints
- Traffic Routing Patterns: Analyzing how data packets travel through the internet
- Crowdsourced Data: Collecting and aggregating user-reported location information
- Machine Learning: Using AI to identify patterns and improve accuracy over time
The data is typically stored in specialized file formats optimized for rapid lookup, such as binary database files (MMDB), CSV files, or proprietary formats. These are designed to balance file size with lookup speed, enabling quick queries even with millions of records.
Types of IP Geolocation Databases
IP geolocation databases come in various forms, each designed to meet different needs and use cases. Understanding the different types can help you select the right solution for your specific requirements.
By Deployment Method
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Local Database Files | Downloadable databases that are installed locally on your servers | High-volume applications, privacy concerns, offline access |
| API Services | Cloud-based lookup services accessed via API calls | Simpler implementation, lower maintenance, always up-to-date |
| Hybrid Solutions | Combination of local databases with API fallback | Balance of performance and accuracy, resilience |
By Data Resolution
| Resolution | Description | Typical Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Country-Level | Identifies only the country associated with the IP | 95-99% |
| Region/State-Level | Identifies country and administrative region/state | 80-90% |
| City-Level | Identifies country, region, and city | 70-80% |
| Postal Code-Level | Includes postal/ZIP code identification | 60-75% |
| Coordinate-Level | Provides latitude/longitude coordinates | Varies widely |
By Licensing Model
| Model | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Free/Open Source | No-cost databases with varied licensing terms | Lower accuracy, less frequent updates, limited support |
| Commercial | Paid databases with licensing fees | Higher accuracy, regular updates, technical support |
| Subscription-Based | Recurring payment model for access | Regular updates, scalable pricing based on usage |
Most providers offer tiered options that combine these various dimensions, allowing you to select the right balance of cost, accuracy, and features for your specific needs. As you move up in tiers, you typically gain access to more detailed information and additional data points beyond basic geolocation.
Top IP Geolocation Database Providers in
The market for IP geolocation services has evolved significantly, with several established providers offering robust solutions. Here’s a comparison of the leading providers in :
| Provider | Key Features | Pricing () | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geo Targetly |
– All-in-one geo targeting platform – Content personalization tools – Geo redirects, popups, and notifications – Easy integration with major platforms |
– Free trial available – Standard plans starting at $9/month – Custom enterprise solutions available | Marketing-focused applications, content personalization, no-code solutions |
| MaxMind GeoIP2 |
– High accuracy at country level – Available as database or web service – Additional fraud prevention tools – Comprehensive metadata |
– GeoIP2 Precision Services: Starts at $20/month – Database licensing: $1,200/year and up | Enterprise solutions, fraud prevention, high-volume applications |
| IPinfo |
– Proprietary Probe Network for accuracy – Privacy detection features – Company and carrier data – Flexible API and databases |
– Free tier: Country-level data – Core: $49/month (150,000 requests) – Plus: $249/month (250,000 requests) – Business: $499/month (500,000 requests) | Developer-friendly applications, businesses needing enriched data beyond location |
| IP2Location |
– Extensive coverage of IPv4 and IPv6 – Multiple data modules – Regular monthly updates – Various file formats supported |
– Database packages: $200/year to $1,800/year – Web service: Custom pricing | Businesses requiring flexible data module selection, comprehensive IPv6 support |
| DB-IP |
– Frequent database updates – IP to company mapping – Comprehensive IPv6 coverage – Multiple file formats |
– Basic API: Starting at €8.29/month – Premium database licenses: Custom pricing | Budget-conscious applications, businesses needing company-level data |
Featured Provider: Geo Targetly
Geo Targetly stands out in as a comprehensive solution that goes beyond simple IP geolocation to provide actionable targeting tools. Their platform enables businesses to create location-specific experiences without complex coding, offering features like:
- Automatic visitor redirection based on location
- Dynamic content display tailored to visitor geography
- Location-specific popups and announcement bars
- Geo-targeted links and short URLs
- IP blocking for geo-restrictions
- JavaScript execution based on visitor location
Their user-friendly interface and integration with major platforms make them particularly valuable for marketing teams and businesses looking to improve conversion rates through location-based personalization.
Try Geo Targetly Free for 14 DaysAccuracy and Limitations of IP Geolocation
While IP geolocation databases are powerful tools, understanding their inherent limitations is crucial for setting realistic expectations and designing effective implementations.
Accuracy Considerations
The accuracy of IP geolocation varies significantly depending on several factors:
As shown in the chart above, accuracy generally decreases as you seek more granular location data. While country-level identification is highly reliable (typically 95-99% accurate), city-level accuracy often drops to 70-80%, and postal code precision can be even lower.
Key Limitations
- IP Address Reassignment: ISPs frequently reassign IP addresses, especially dynamic IPs, making some database entries outdated between updates.
- Network Architecture: Corporate networks may route traffic through central gateways, making all users appear to be in a single location regardless of their actual distribution.
- Mobile Networks: Mobile device IPs often resolve to cellular network access points rather than actual device locations, sometimes showing locations hundreds of miles from the user.
- VPNs and Proxies: Virtual Private Networks and proxy servers mask users’ true locations, showing the exit node location instead.
- Rural Areas: Geolocation tends to be less accurate in rural or less densely populated regions with fewer data points.
- IPv6 Coverage: Some databases have less comprehensive data for IPv6 addresses compared to IPv4.
Improving Accuracy
While these limitations exist, several strategies can help improve the effectiveness of IP geolocation:
- Use multiple data sources to cross-reference and validate location information
- Implement VPN and proxy detection to identify potentially misleading IP addresses
- Choose providers with frequent updates to minimize inaccuracies from IP reassignments
- Supplement with browser-based geolocation when higher precision is needed and user consent is possible
- Consider fallback strategies for cases where location cannot be reliably determined
Understanding these limitations helps set appropriate expectations and design systems that gracefully handle edge cases where geolocation may be inaccurate or unavailable.
Implementation Methods
Implementing IP geolocation technology into your systems can be approached in several ways, each with distinct advantages depending on your technical requirements, budget constraints, and use cases.
1. API Integration
API-based implementations involve making HTTP requests to a geolocation service provider to retrieve location data on demand.
// Example JavaScript code for API implementation
fetch('https://ipinfo.io/json?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log('IP Geolocation Data:', data);
// Use data.country, data.region, data.city, etc.
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error fetching IP info:', error);
});Advantages:
- No database maintenance required
- Always up-to-date information
- Minimal local resource requirements
- Simple to implement and scale
Disadvantages:
- Dependency on external service availability
- API rate limits and potential costs per request
- Network latency for each lookup
- Privacy considerations for sending IP data to third parties
2. Local Database Integration
This approach involves downloading and periodically updating a geolocation database that is hosted on your own infrastructure.
// Example PHP code for local database implementation
require_once 'vendor/autoload.php';
use MaxMind\Db\Reader;
// Open the GeoIP2 database file
$reader = new Reader('/path/to/GeoIP2-City.mmdb');
// Look up the IP address
$record = $reader->get($_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']);
// Access the data
$country = $record['country']['names']['en'];
$city = $record['city']['names']['en'];
$latitude = $record['location']['latitude'];
$longitude = $record['location']['longitude'];
// Close the database connection
$reader->close();Advantages:
- Fast lookups with minimal latency
- No external dependencies once loaded
- No per-query costs
- Better privacy control as data stays within your infrastructure
- Works in offline environments
Disadvantages:
- Requires regular updates to maintain accuracy
- Consumes server storage and memory resources
- Initial setup complexity
- May require additional licensing fees
3. CDN or Cloud Provider Integration
Many Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and cloud providers offer built-in geolocation capabilities that can be leveraged through their platforms.
// Example Cloudflare Worker script
addEventListener('fetch', event => {
event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request))
})
async function handleRequest(request) {
// CF-IPCountry header is automatically added by Cloudflare
const countryCode = request.headers.get('CF-IPCountry')
if (countryCode === 'US') {
return new Response('Hello, American visitor!')
} else {
return new Response('Hello, international visitor from ' + countryCode)
}
}Advantages:
- Minimal implementation effort
- Edge-based processing for low latency
- Often included in existing CDN services
- Scalable with your infrastructure
Disadvantages:
- Limited to the data fields provided by the platform
- Less control over data sources and update frequency
- Vendor lock-in concerns
- May require using specific cloud services
4. JavaScript Client-Side Implementation
For web applications, client-side JavaScript can be used to determine visitor location through geolocation services.
// Example using Geo Targetly's client-side implementation
<script src="https://cdn.geotargetly.com/geo.min.js"></script>
<script>
GeoTargetly.addEventListener('ready', function() {
// Access visitor's location data
console.log('Country:', GeoTargetly.data.country);
console.log('Region:', GeoTargetly.data.region);
console.log('City:', GeoTargetly.data.city);
// Personalize content based on location
if (GeoTargetly.data.country === 'US') {
document.getElementById('pricing').innerHTML = '$99';
} else if (GeoTargetly.data.country === 'GB') {
document.getElementById('pricing').innerHTML = '£75';
}
});
</script>Advantages:
- Simple to implement for web applications
- Reduces server-side processing
- Enables dynamic content without page reloads
- Works with static websites
Disadvantages:
- Visible to users who can inspect the code
- Subject to client-side manipulation
- May be blocked by browsers or extensions
- Adds loading time to web pages
Implementation Best Practices:
- Cache results when possible to reduce redundant lookups
- Implement proper error handling for failed lookups
- Consider a hybrid approach using local database with API fallback
- Test thoroughly with various IP types (IPv4, IPv6, mobile, etc.)
- Set up monitoring to detect and address accuracy issues
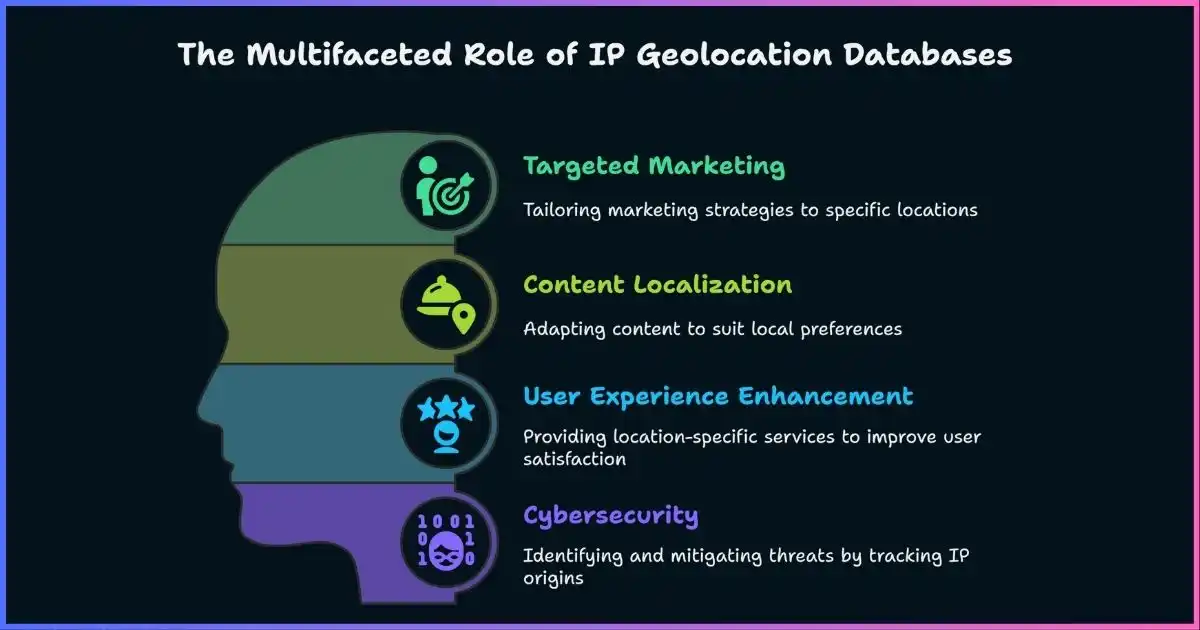
Use Cases and Applications
IP geolocation databases power a wide range of applications across industries. Understanding these use cases can help you identify potential implementations for your own business.
Content Personalization
Deliver location-relevant content to visitors automatically, enhancing user experience and engagement.
- Localized language and currency
- Regional promotions and offerings
- Location-specific landing pages
- Weather-based content adjustments
“Implementing IP geolocation for content personalization increased our conversion rates by 26% for international visitors.” – E-commerce Director
Fraud Prevention & Security
Detect suspicious activities based on unexpected or high-risk locations.
- Login attempt verification
- Transaction risk assessment
- Account takeover prevention
- Identifying suspicious traffic patterns
“IP geolocation helped us reduce fraudulent transactions by 37% by flagging unusual access locations.” – Cybersecurity Analyst
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to region-specific regulations and restrictions.
- GDPR compliance for EU visitors
- Geo-restricted content distribution
- Age verification requirements by country
- Tax and pricing compliance
“Our legal team relies on IP geolocation to automatically apply the appropriate regulatory frameworks based on visitor location.” – Compliance Officer
Targeted Advertising
Deliver geographically relevant advertisements to increase relevance and conversion rates.
- Local store promotions
- Regional product offerings
- Location-based bid adjustments
- Seasonally appropriate messaging
“Location-based ad targeting improved our click-through rates by 43% and reduced ad spend wastage.” – Digital Marketing Manager
Traffic Analysis & Business Intelligence
Gain insights into visitor demographics and behavior patterns by geography.
- Geographic traffic distribution
- Regional conversion rate analysis
- Market penetration assessment
- International expansion planning
“Geolocation data revealed unexpected market opportunities in regions we hadn’t been actively targeting.” – Business Analyst
Digital Rights Management
Control access to digital content based on geographic licensing agreements.
- Streaming media restrictions
- Software license enforcement
- Publishing rights management
- Event broadcasting limitations
“IP geolocation enables us to honor our complex international licensing agreements while maximizing content availability.” – Content Distribution Director
Industry-Specific Applications
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| E-commerce |
– Automatic currency conversion – Local shipping options and tax calculation – Regional product availability – Location-based promotions |
| Financial Services |
– Fraud detection and prevention – KYC (Know Your Customer) verification – Regulatory compliance by jurisdiction – Location-based risk assessment |
| Media & Entertainment |
– Content licensing enforcement – Regional advertising partnerships – Location-based content recommendations – Market-specific pricing models |
| SaaS & Technology |
– Data sovereignty compliance – CDN optimization – Server selection for minimal latency – Global availability monitoring |
| Healthcare |
– Regional regulatory compliance – Geographic health trend analysis – Provider network recommendations – Telemedicine service restrictions |
Implementation Example: E-commerce Product Pages
An online retailer might use IP geolocation to enhance their product pages in several ways:
- Display prices in the visitor’s local currency
- Show accurate shipping times and costs based on location
- Present size guides using local measurement systems
- Highlight products popular in the visitor’s region
- Display location-appropriate seasonal merchandise
- Indicate local availability and nearby physical stores
These enhancements create a more personalized shopping experience that increases conversion rates and reduces cart abandonment.
Explore Geo Targeting SolutionsMarket Growth and Statistics
The IP geolocation database market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for location-based services, personalization, and security solutions. Let’s examine the key statistics and trends shaping this market in .
Market Size and Projections
Source: Data Insights Market Research, HTF Market Intelligence
As illustrated in the chart above, the global IP geolocation market is experiencing robust growth. Valued at approximately $5 billion in 2025, the market is projected to reach $11.1 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15%.
Key Growth Drivers
Increased Digital Transformation
The accelerated pace of digital transformation across industries has amplified the need for location-aware applications and services, driving demand for accurate geolocation data.
Rising Cybersecurity Concerns
As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations are increasingly incorporating location intelligence into their security frameworks to detect and prevent suspicious activities.
Personalization Demand
Consumer expectations for personalized experiences have prompted businesses to implement location-based customization, boosting the adoption of geolocation technologies.
Regulatory Compliance
Evolving privacy regulations and region-specific legal requirements have necessitated the use of geolocation data for compliance management across global operations.
Industry Adoption Rates
Source: Market analysis of IP geolocation implementation by industry
Regional Market Distribution
Source: Global IP Geolocation Market Analysis
Key Market Statistics for
- Market Size: $5 billion globally
- Projected CAGR: 15% from 2025 to 2033
- Number of Major Providers: 15+ established vendors
- IP Records Processed Daily: 500+ billion lookups across all providers
- Most Rapidly Growing Segment: Mobile IP geolocation services (22% YoY growth)
- Dominant Deployment Method: API services (58% of market share)
- Fastest Growing Use Case: Fraud prevention and security (31% growth)
Future Trends in IP Geolocation
The IP geolocation landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with several emerging trends poised to shape the future of this technology. Understanding these developments can help businesses prepare for upcoming changes and opportunities.
AI-Enhanced Accuracy
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing IP geolocation by analyzing vast datasets to identify patterns that improve location precision. These advanced algorithms can:
- Identify anomalies in traditional geolocation methods
- Dynamically adjust location predictions based on real-time network data
- Incorporate auxiliary data sources for enhanced accuracy
- Adapt to changing network topologies more efficiently
By 2027, AI-driven geolocation is expected to improve city-level accuracy by up to 15% compared to traditional methods.
Privacy-Centric Approaches
As privacy regulations continue to strengthen globally, IP geolocation providers are developing new approaches that balance accuracy with privacy compliance:
- Differential privacy techniques to add controlled noise to datasets
- Aggregated location data that avoids individual identification
- On-device processing options that minimize data transfer
- Transparent data collection and usage policies
These approaches will be particularly important as regulations like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California continue to influence global privacy standards.
IPv6 Expansion
The ongoing transition to IPv6 addresses is creating both challenges and opportunities for geolocation services:
- Vastly increased address space requiring new mapping approaches
- More stable assignments potentially improving long-term accuracy
- New allocation patterns that may provide better geographic signals
- Specialized IPv6 databases with improved precision
By 2026, IPv6 traffic is expected to account for over 60% of internet traffic, making comprehensive IPv6 geolocation capabilities increasingly critical.
Edge Computing Integration
Edge computing architectures are creating new possibilities for IP geolocation implementation:
- Geolocation processing at network edge points for reduced latency
- Local database caching for faster repeat lookups
- Distributed geolocation systems that balance load and improve reliability
- Location-aware edge routing that optimizes content delivery
This trend aligns with the broader shift toward decentralized computing and will enable faster, more reliable geolocation services.
Emerging Use Cases
Beyond current applications, several emerging use cases are expanding the potential of IP geolocation:
| Emerging Use Case | Description | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Augmented Reality Content | Location-aware AR experiences that adapt to user geography | Growing rapidly with 40% annual increase in implementation |
| Autonomous Systems | Self-driving vehicles and drones using IP geolocation as a backup positioning system | Early-stage development with significant growth expected by 2027 |
| Climate-Adaptive Services | Applications that adjust functionality based on local climate conditions | Increasing adoption in energy, agriculture, and smart city sectors |
| Cross-Border E-commerce | Automated customs, duties, and regulatory compliance for international sales | Critical growth area with 35% annual increase in solution adoption |
Preparing for the Future
To stay ahead of these evolving trends, businesses should consider:
- Evaluating current geolocation implementations against emerging standards
- Selecting providers with robust IPv6 support and privacy-compliant approaches
- Exploring hybrid systems that combine different geolocation methods
- Monitoring regulatory developments that may impact geolocation practices
- Considering adaptable implementations that can incorporate new data sources
Frequently Asked Questions
Accuracy varies by level of detail. Country-level identification is typically 95-99% accurate, while city-level accuracy ranges from 70-80%. Postal code precision is generally lower at 60-75%. Accuracy is influenced by factors such as IP reassignment frequency, network architecture, and data freshness. Mobile networks and rural areas tend to have lower accuracy compared to urban fixed-line connections.
IP geolocation will typically return the location of the VPN or proxy server’s exit node, not the user’s actual location. Some advanced geolocation services include VPN and proxy detection capabilities that can flag such connections, though they generally cannot determine the user’s true location behind these services. For businesses concerned about VPN usage, combining geolocation with additional verification methods is recommended.
Most commercial providers update their databases weekly or monthly to account for IP reassignments and network changes. For optimal accuracy, local database implementations should be updated at least monthly, though more frequent updates (weekly or even daily) are recommended for applications where precision is critical. API-based solutions typically use the most current data automatically without requiring manual updates.
Yes, several legal and privacy considerations exist. IP addresses may be considered personal data under regulations like GDPR, requiring proper consent and data handling procedures. Additionally, some jurisdictions restrict certain uses of geolocation data or require specific disclosures. Best practices include transparently informing users about geolocation usage, providing opt-out options where feasible, and ensuring compliance with relevant privacy regulations in both the user’s location and your operating regions.
API solutions involve making real-time requests to a third-party service that returns location data. They require no maintenance, are always up-to-date, but add network latency and typically have usage limits or per-query costs. Database solutions involve downloading geolocation data to your own infrastructure, offering faster lookups without external dependencies, but requiring regular updates and more initial setup. Many organizations use a hybrid approach, with local databases for common lookups and API fallbacks for edge cases or when higher accuracy is needed.
IP geolocation is less precise than GPS but requires no user permission and works server-side. GPS offers meter-level accuracy but requires device hardware and explicit user consent. Browser-based geolocation combines multiple sources (GPS, Wi-Fi, cell towers, IP) for good accuracy but also requires user permission. IP geolocation is ideal for backend systems, initial location estimates, and scenarios where user interaction isn’t possible, while GPS and browser geolocation are better for applications requiring precise positioning and where user consent is obtainable.
Generally, no. Standard IP geolocation is not precise enough to identify specific households, and certainly not individuals. Most residential users share IP addresses with others in their area, and many ISPs regularly reassign dynamic IPs. The typical precision limit is at the neighborhood or postal code level at best. Some premium services claim higher precision, but these should be used with caution and in compliance with privacy regulations. For identifying specific users, businesses typically need to combine IP geolocation with account information or other identifiers.
Key factors to consider include: accuracy levels at different geographic resolutions; coverage of both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses; update frequency; data sources and methodology; additional data fields beyond basic location; performance and scalability; pricing model and cost predictability; technical support and documentation quality; and compliance with relevant privacy regulations. It’s also worth evaluating whether you need advanced features like VPN detection, ASN information, or time zone data based on your specific use cases.
Mobile networks present unique challenges for IP geolocation. Mobile IP addresses typically map to cellular network gateways rather than the device’s physical location, sometimes showing locations hundreds of miles from the actual user. As users move between cell towers, their traffic may still route through distant network aggregation points. Additionally, mobile carriers frequently reassign IP addresses. For applications requiring precise mobile user locations, supplementary methods like GPS or cell tower triangulation are recommended instead of relying solely on IP geolocation.
While technically possible, building a comprehensive IP geolocation database requires significant resources, specialized knowledge, and ongoing maintenance. The process involves collecting vast amounts of IP routing data, establishing relationships with ISPs, implementing complex triangulation algorithms, and continuously validating and updating the information. For most organizations, purchasing access to established commercial databases or APIs is more cost-effective and reliable than attempting to build and maintain their own solution.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of IP Geolocation
IP geolocation databases have become an essential technology for businesses seeking to deliver personalized experiences, enhance security, ensure regulatory compliance, and gain valuable location-based insights. As we’ve explored throughout this guide, these powerful tools offer diverse applications across industries, from e-commerce and financial services to media and healthcare.
While understanding the limitations of IP geolocation is important—particularly regarding accuracy levels and challenges with mobile networks, VPNs, and proxies—the technology continues to evolve with improvements in AI-driven analysis, privacy-centric approaches, and IPv6 support. The robust market growth projected through 2033 reflects the increasing value businesses are finding in location intelligence.
Whether you’re implementing IP geolocation for the first time or looking to enhance your existing approach, selecting the right provider and deployment method is critical. Consider your specific accuracy requirements, integration preferences, budget constraints, and use cases when evaluating options like MaxMind, IPinfo, IP2Location, or Geo Targetly.
Disclosure: We may earn commission for purchases that are made by visitors on this site at no additional cost on your end. All information is for educational purposes and is not intended for financial advice. Read our affiliate disclosure.