Split Tunneling vs Full Tunneling: Complete VPN Guide
Understanding the key differences between split tunneling and full tunneling VPN configurations is crucial for choosing the right VPN setup for your security and performance needs. This comprehensive guide explores both approaches, comparing their benefits, drawbacks, and ideal use cases to help you make an informed decision about which VPN tunneling method best suits your requirements.
Table of Contents
Understanding VPN Tunneling Methods
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become essential tools for online privacy and security, but not all VPN configurations are created equal. The choice between split tunneling and full tunneling can significantly impact your internet experience, security level, and overall performance. With VPN usage surging by 124% during the COVID-19 pandemic according to recent statistics, understanding these tunneling methods has never been more important.
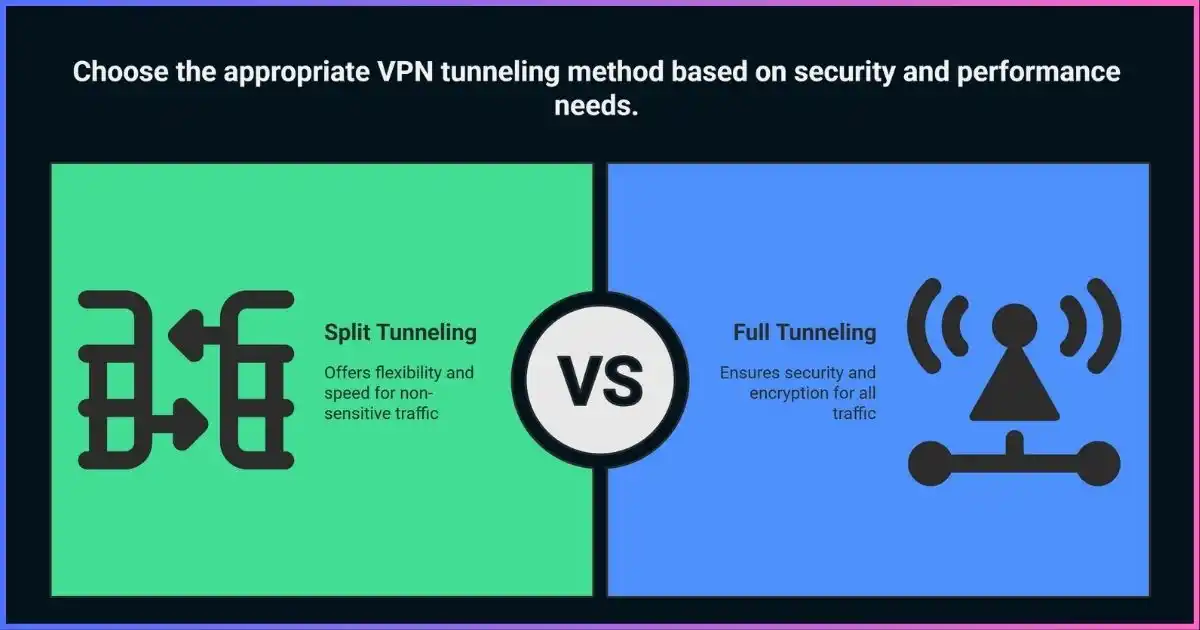
Split tunneling and full tunneling represent two fundamentally different approaches to routing your internet traffic. While full tunneling encrypts and routes all your internet traffic through a VPN server, split tunneling allows you to selectively choose which applications and traffic go through the VPN tunnel while others access the internet directly.
This comprehensive guide examines both approaches in detail, providing you with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision about which VPN tunneling method best suits your specific needs and use cases.
What is Full Tunneling?
Full tunneling is a VPN configuration where all your internet traffic is routed through the VPN server. This means every data packet that leaves your device—whether it’s web browsing, email, streaming, or any other online activity—is encrypted and sent through the secure VPN tunnel before reaching its destination.
When you activate a full tunnel VPN, your device establishes a single encrypted connection to the VPN server, and all subsequent internet traffic flows through this secure channel. This provides maximum security and privacy for all your online activities, as your internet service provider (ISP), government agencies, and potential hackers cannot monitor or intercept your data.
Key Characteristics of Full Tunneling:
- All internet traffic is encrypted and routed through the VPN
- Single point of connection to the VPN server
- Complete IP address masking for all online activities
- Maximum privacy and security protection
- Simplified configuration and management
Full tunneling is the default configuration for most VPN services and is often recommended for users who prioritize security and privacy above all else. However, this approach can impact internet speed and may restrict access to local network resources.
What is Split Tunneling?
Split tunneling is a VPN feature that allows you to divide your internet traffic into two separate paths: some traffic goes through the encrypted VPN tunnel, while other traffic accesses the internet directly through your regular connection. This selective routing gives you greater control over which applications and services use the VPN protection.
With split tunneling, you can configure your VPN to protect sensitive activities like work communications, banking, or private browsing while allowing other activities like streaming local content, gaming, or accessing local network devices to bypass the VPN for better performance.
Types of Split Tunneling:
- App-based split tunneling: Choose specific applications to use or bypass the VPN
- URL-based split tunneling: Route specific websites through or around the VPN
- Inverse split tunneling: Exclude certain apps from VPN protection while routing everything else through the tunnel
Split tunneling offers a balanced approach between security and performance, making it ideal for users who need VPN protection for specific activities while maintaining fast, direct access to other services.
VPN Usage Statistics 2024
Understanding current VPN usage patterns helps contextualize the importance of choosing the right tunneling method. Recent research reveals significant trends in how people use VPNs and their preferences for different configurations.
54%
of Americans don’t use VPNs
124%
VPN usage increase during COVID-19
55%
VPN usage rate in Indonesia (highest globally)
The data shows that while VPN adoption is growing, many users still lack awareness of advanced features like split tunneling. Among VPN users, 29% use VPNs for personal use only, 24% for business use only, and 15% for both personal and business purposes.
Detailed Comparison: Split vs Full Tunneling
| Feature | Split Tunneling | Full Tunneling |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Selective – only chosen traffic encrypted | Complete – all traffic encrypted |
| Performance | Faster for non-VPN traffic | Slower due to encryption overhead |
| Security Level | Moderate – depends on configuration | Maximum – all traffic protected |
| Bandwidth Usage | Lower VPN bandwidth consumption | Higher VPN bandwidth usage |
| Local Network Access | Easy access to local resources | Limited local network access |
| Configuration Complexity | More complex setup required | Simple, one-click setup |
| Use Case Flexibility | High – customizable for different needs | Low – one-size-fits-all approach |
Performance Analysis
Performance is a crucial factor when choosing between split and full tunneling. The impact on speed, latency, and overall user experience can vary significantly depending on your usage patterns and requirements.
Split Tunneling Performance
- Non-VPN traffic maintains full ISP speed
- Reduced latency for local connections
- Better streaming performance for local content
- Optimized gaming experience
- Lower overall bandwidth consumption
Full Tunneling Performance
- All traffic subject to VPN server limitations
- Increased latency for all connections
- Potential speed reduction of 10-30%
- Higher server load and bandwidth usage
- May impact real-time applications
Performance testing shows that split tunneling can improve overall user experience by allowing time-sensitive applications to bypass the VPN while maintaining security for critical traffic. However, the actual performance benefit depends on your specific use case and VPN provider’s infrastructure.
Security Considerations
Security is the primary reason most people use VPNs, but the choice between split and full tunneling creates different security profiles that must be carefully considered.
Full Tunneling Security Benefits
- Complete traffic encryption and protection
- All IP addresses hidden from ISPs and third parties
- Comprehensive protection against DNS leaks
- Simplified security model with fewer vulnerabilities
- Protection from local network attacks
Split Tunneling Security Considerations
- Non-VPN traffic exposed to ISP monitoring
- Potential for DNS leaks on direct connections
- Risk of malware affecting non-protected traffic
- Complex configuration may introduce vulnerabilities
- Partial IP address exposure
Security Statistics
- 80% of cyberattacks target remote users and devices
- 93% of organizations experienced data breaches due to remote work during the pandemic
- 74% of businesses consider VPN security a top priority
While split tunneling offers flexibility and performance benefits, it requires careful configuration to maintain security. Organizations should implement strict policies about which traffic can bypass the VPN and regularly audit their split tunneling configurations.
Use Cases and Scenarios
Understanding when to use each tunneling method depends on your specific needs, security requirements, and performance expectations. Here are common scenarios for each approach.
Best Use Cases for Split Tunneling
- Remote work accessing company resources while streaming local content
- Online gaming with secure communication apps
- Accessing local network devices while browsing securely
- Bandwidth-sensitive applications requiring direct connection
- Services that block VPN connections
Best Use Cases for Full Tunneling
- Public Wi-Fi usage in cafes, airports, hotels
- Handling highly sensitive or confidential data
- Accessing geo-blocked content from different regions
- Maximum privacy for all online activities
- Avoiding ISP throttling and monitoring
Business Considerations
For businesses, the choice between split and full tunneling involves balancing security requirements, employee productivity, and IT management complexity. Recent statistics show that 28% of VPN users utilize VPNs for business purposes only, while 22% use them for both personal and business activities.
Cost Efficiency
Split tunneling reduces bandwidth costs by routing only necessary traffic through VPN servers
Employee Productivity
Direct internet access for non-sensitive tasks improves performance and user experience
Compliance Requirements
Some industries require full tunneling for regulatory compliance and data protection
Implementation Recommendations
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment before implementing split tunneling
- Establish clear policies about which traffic can bypass the VPN
- Implement monitoring tools to track split tunneling usage
- Provide employee training on proper VPN configuration
- Regular security audits of split tunneling configurations
Business adoption of split tunneling continues to grow as organizations recognize its benefits for remote work scenarios. However, implementation requires careful planning and ongoing management to maintain security standards.
Related: VPN Logging Policies
Related: How to Unblock Websites with VPNs or Proxies
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between split tunneling and full tunneling?
The main difference is that full tunneling routes all your internet traffic through the VPN server, providing complete encryption and protection, while split tunneling allows you to choose which applications and traffic go through the VPN while others access the internet directly.
Is split tunneling less secure than full tunneling?
Split tunneling can be less secure because traffic that bypasses the VPN is not encrypted and may be visible to your ISP and other third parties. However, when properly configured, split tunneling can provide adequate security for most use cases while offering better performance.
Does split tunneling improve internet speed?
Yes, split tunneling can improve internet speed for applications that bypass the VPN because they connect directly to the internet without the encryption overhead and routing through VPN servers. However, traffic going through the VPN will still experience the usual speed reduction.
Can I use split tunneling for streaming services?
Yes, split tunneling is excellent for streaming services. You can route streaming apps through your direct internet connection for better performance while keeping other sensitive activities protected through the VPN tunnel.
Which VPN providers offer split tunneling?
Many major VPN providers offer split tunneling, including NordVPN, ExpressVPN, Surfshark, and CyberGhost. The implementation and features may vary between providers, so it’s important to check the specific capabilities of each service.
Is split tunneling suitable for business use?
Split tunneling can be suitable for business use, but it requires careful planning and implementation. Businesses should establish clear policies about which traffic can bypass the VPN and implement monitoring tools to ensure compliance with security requirements.
Can I configure split tunneling on mobile devices?
Yes, most modern VPN apps for iOS and Android support split tunneling. You can typically configure it through the app settings to choose which apps use the VPN and which connect directly to the internet.
What are the potential risks of split tunneling?
The main risks include exposure of non-VPN traffic to ISP monitoring, potential DNS leaks, increased vulnerability to malware for unprotected traffic, and complexity in configuration that may introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly managed.
Conclusion
The choice between split tunneling and full tunneling ultimately depends on your specific needs, security requirements, and performance expectations. Full tunneling provides maximum security and privacy for all your online activities, making it ideal for users who prioritize complete protection over performance. This approach is particularly recommended when using public Wi-Fi, handling sensitive data, or requiring comprehensive anonymity.
Split tunneling offers a more flexible approach that balances security with performance, allowing you to protect sensitive traffic while maintaining fast, direct access to other services. This configuration is excellent for remote work scenarios, gaming, streaming, and situations where you need to access local network resources while maintaining VPN protection for specific applications.
With VPN usage continuing to grow and remote work becoming increasingly common, understanding these tunneling methods is crucial for making informed decisions about your online security and privacy. Both approaches have their place in the modern digital landscape, and the best choice depends on your individual circumstances and requirements.
As you consider implementing either split or full tunneling, remember that proper configuration and regular security audits are essential regardless of which approach you choose. The key is to find the right balance between security, performance, and usability for your specific use case.
Disclosure: We may earn commission for purchases that are made by visitors on this site at no additional cost on your end. All information is for educational purposes and is not intended for financial advice. Read our affiliate disclosure.