How VPNs Work: A Beginner’s Guide to Virtual Private Networks
Master the fundamentals of VPN technology and protect your digital privacy
Understanding how VPNs work is crucial in today’s digital landscape where online privacy and security have become paramount concerns. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet, protecting your data from prying eyes and cyber threats. This comprehensive VPN explained guide will walk you through everything you need to know about virtual private network technology, from basic concepts to advanced features, helping you make informed decisions about your online security.
With over 1.75 billion people worldwide using VPNs and cybersecurity threats costing businesses an average of $4.88 million per data breach in , understanding VPN technology has never been more important. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to deepen your knowledge, this virtual private network tutorial covers the essential concepts, protocols, and practical applications that will help you navigate the world of online privacy protection.
1.75B
Global VPN Users
46%
Americans Using VPNs
$4.88M
Average Data Breach Cost
Table of Contents
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and a remote server operated by a VPN service provider. Think of it as a private tunnel through the public internet that shields your online activities from surveillance, hackers, and other threats.
When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic is routed through this encrypted tunnel to the VPN server, which then forwards your requests to the intended destination. This process masks your real IP address and location, making it appear as though you’re browsing from the VPN server’s location instead of your actual location.
The fundamental purpose of a VPN is to provide privacy, security, and anonymity online. It accomplishes this through sophisticated encryption protocols that scramble your data, making it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it, including internet service providers, government agencies, hackers, and other malicious actors.
How VPNs Work: Technical Overview
Understanding how VPNs work requires grasping the fundamental concept of tunneling and encryption. When you activate a VPN connection, several technical processes occur simultaneously to secure your internet traffic.
The VPN Connection Process
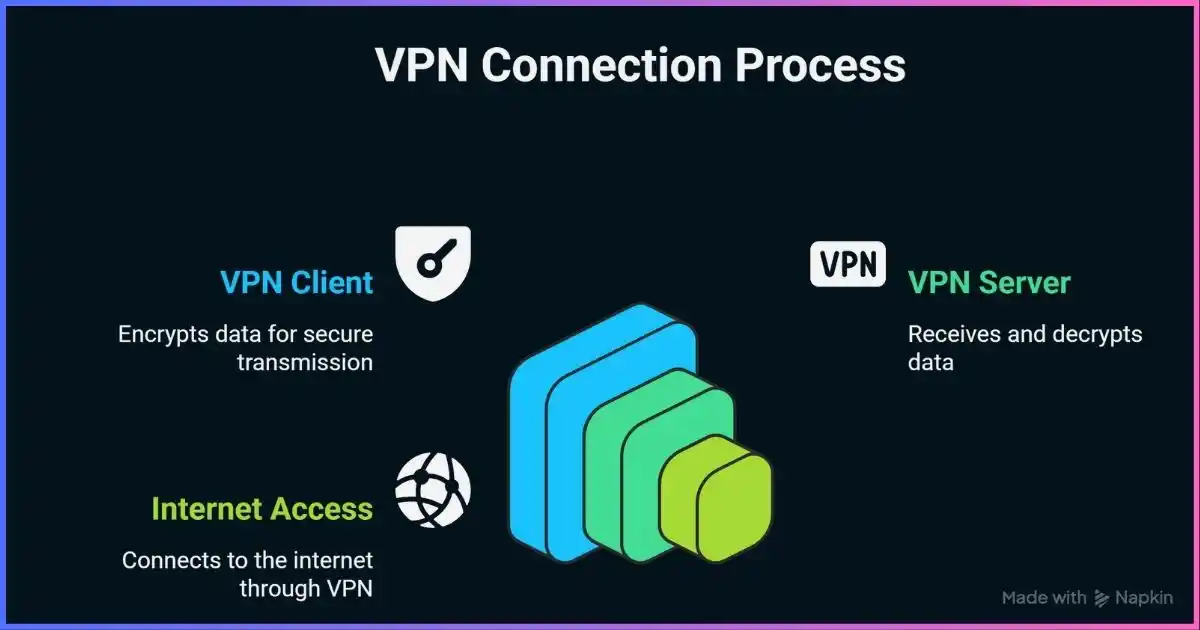
The VPN connection process begins when your device initiates a connection to a VPN server. Your VPN client software establishes a secure handshake with the server, during which both parties authenticate each other and agree on encryption parameters. This negotiation process ensures that only authorized users can access the VPN service.
Once the connection is established, all your internet traffic is encapsulated within encrypted packets before being sent to the VPN server. The server then decrypts these packets and forwards your requests to their intended destinations on the internet. Response data follows the reverse path, being encrypted at the server and decrypted at your device.
Data Routing and IP Masking
One of the most significant aspects of how VPNs work is their ability to mask your real IP address. When websites and online services see your traffic, they identify the VPN server’s IP address rather than your actual device’s IP address. This process provides anonymity and allows you to appear as though you’re browsing from a different geographical location.
The VPN server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. All your DNS requests, web browsing, file downloads, and other internet activities are processed through this server, creating a layer of separation between your real identity and your online activities.
The Encryption Process
Encryption is the cornerstone of VPN technology, transforming readable data into scrambled code that can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key. Modern VPNs employ military-grade encryption standards to ensure maximum security for user data.
Encryption Standards
The most widely used encryption standard in VPN technology is Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with 256-bit keys, often referred to as AES-256. This encryption method is considered virtually unbreakable and is used by government agencies, financial institutions, and security-conscious organizations worldwide.
AES-256 encryption works by converting your data into ciphertext using a complex mathematical algorithm and a 256-bit encryption key. The strength of this encryption lies in the astronomical number of possible key combinations – approximately 2^256 possibilities, making brute force attacks computationally infeasible even with supercomputers.
Key Exchange and Authentication
Before encrypted communication can begin, VPN clients and servers must securely exchange encryption keys. This process typically uses public-key cryptography, where each party has a pair of mathematically related keys: a public key that can be shared openly and a private key that must be kept secret.
The key exchange process ensures that even if malicious actors intercept the initial communication, they cannot determine the encryption keys being used. Modern VPNs also implement perfect forward secrecy, which generates new encryption keys for each session, ensuring that even if one key is compromised, historical data remains secure.
VPN Protocols Comparison
VPN protocols define how data is transmitted between your device and the VPN server. Different protocols offer varying levels of security, speed, and compatibility. Understanding these protocols helps you choose the right VPN service for your specific needs.
| Protocol | Security Level | Speed | Compatibility | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | Very High | Good | Excellent | General purpose, maximum security |
| WireGuard | Very High | Excellent | Good | Modern applications, speed priority |
| IKEv2/IPSec | High | Very Good | Good | Mobile devices, network switching |
| L2TP/IPSec | High | Moderate | Very Good | Legacy systems, broad compatibility |
| PPTP | Low | Excellent | Excellent | Legacy support only (not recommended) |
OpenVPN: The Gold Standard
OpenVPN is widely considered the gold standard for VPN protocols due to its exceptional security, flexibility, and open-source nature. It uses SSL/TLS protocols for key exchange and supports both UDP and TCP protocols for data transmission. OpenVPN’s ability to bypass firewalls and its extensive configuration options make it suitable for both personal and enterprise use.
WireGuard: The Modern Alternative
WireGuard represents the next generation of VPN protocols, offering significantly improved performance while maintaining high security standards. With only 4,000 lines of code compared to OpenVPN’s 400,000+ lines, WireGuard is easier to audit and potentially more secure. It provides faster connection speeds and better battery life on mobile devices.
Types of VPNs
VPNs can be categorized into several types based on their intended use, deployment method, and target audience. Understanding these different types helps you choose the most appropriate VPN solution for your specific requirements.
Remote Access VPNs
Remote Access VPNs are designed for individual users who need to connect securely to a private network from a remote location. These VPNs are commonly used by employees working from home, travelers accessing company resources, or individuals seeking to protect their privacy while using public internet connections.
This type of VPN creates a secure connection between the user’s device and the organization’s network, allowing remote access to internal resources such as files, applications, and databases. Remote Access VPNs typically use client software installed on the user’s device to establish and manage the connection.
Site-to-Site VPNs
Site-to-Site VPNs, also known as network-to-network VPNs, connect entire networks rather than individual devices. These VPNs are primarily used by businesses with multiple locations to create secure connections between different office networks, effectively creating a single, unified network infrastructure.
Site-to-Site VPNs can be further divided into intranet-based and extranet-based VPNs. Intranet-based VPNs connect multiple locations within the same organization, while extranet-based VPNs allow different organizations to share certain resources securely.
Commercial VPN Services
Commercial VPN services are subscription-based services that provide VPN access to individual consumers and businesses. These services operate extensive networks of servers worldwide, allowing users to choose from multiple server locations and enjoy features like geo-location spoofing, streaming optimization, and enhanced privacy protection.
Commercial VPN providers handle all the technical aspects of VPN operation, including server maintenance, security updates, and customer support. This makes them an ideal choice for users who want VPN benefits without the complexity of setting up and managing their own VPN infrastructure.
Key Benefits and Use Cases
VPNs offer numerous benefits that extend beyond basic privacy protection. Understanding these advantages helps you maximize the value of your VPN investment and identify scenarios where VPN usage is particularly beneficial.
Privacy and Anonymity
The primary benefit of VPN usage is enhanced privacy and anonymity online. By encrypting your internet traffic and masking your IP address, VPNs prevent internet service providers, government agencies, hackers, and other third parties from monitoring your online activities. This protection is especially crucial when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured and vulnerable to eavesdropping.
VPNs also help protect against various tracking methods used by advertisers and data brokers. By hiding your real IP address and location, VPNs make it more difficult for these entities to build comprehensive profiles of your online behavior and preferences.
Geo-restriction Bypass
Many online services and content platforms implement geo-restrictions that limit access based on the user’s geographical location. VPNs can help bypass these restrictions by allowing you to appear as though you’re browsing from a different country or region.
This capability is particularly valuable for travelers who want to access their home country’s content while abroad, or for users who want to access region-specific services and information. However, it’s important to note that bypassing geo-restrictions may violate the terms of service of certain platforms.
Enhanced Security for Remote Work
With the rise of remote work, VPNs have become essential tools for maintaining business security. Remote Access VPNs allow employees to securely connect to company networks from any location, ensuring that sensitive business data remains protected during transmission.
VPNs also help organizations maintain compliance with data protection regulations by ensuring that all communications between remote workers and company systems are encrypted and secure. This is particularly important for industries handling sensitive information such as healthcare, finance, and legal services.
How to Choose the Right VPN
Selecting the appropriate VPN service requires careful consideration of multiple factors including security features, performance, compatibility, and cost. The right choice depends on your specific needs, technical expertise, and usage patterns.
Essential Features to Consider
When evaluating VPN services, prioritize providers that offer strong encryption standards, multiple protocol options, and a proven no-logs policy. Look for services that use AES-256 encryption, support modern protocols like WireGuard or OpenVPN, and have undergone independent security audits.
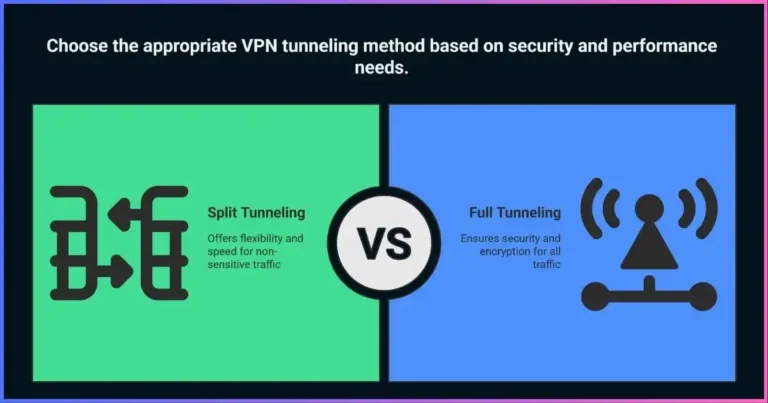
Server network size and distribution are also crucial factors. A larger server network provides better performance, more location options, and improved reliability. Additionally, consider features like kill switches, DNS leak protection, and split tunneling, which enhance security and provide greater control over your VPN connection.
Performance and Reliability
VPN performance can significantly impact your internet experience, so it’s essential to choose a service that offers fast connection speeds and reliable uptime. Look for providers that offer unlimited bandwidth, minimal speed reduction, and consistent performance across different server locations.
Consider the provider’s infrastructure quality, including the use of physical servers versus virtual servers, server load balancing, and network optimization techniques. These factors directly impact connection speed, stability, and overall user experience.
Privacy and Logging Policies
A VPN’s privacy policy and logging practices are fundamental to its effectiveness as a privacy tool. Choose providers with clear, comprehensive no-logs policies that have been independently verified through audits or legal challenges.
Examine the provider’s jurisdiction and legal environment, as this affects what information they may be compelled to collect or share with authorities. Providers based in privacy-friendly jurisdictions with strong data protection laws generally offer better privacy protection.
Setting Up Your VPN
Setting up a VPN is typically a straightforward process that can be completed in minutes. Most commercial VPN providers offer user-friendly applications for various devices and operating systems, making the setup process accessible to users of all technical skill levels.
Installation Process
The installation process begins with choosing a VPN provider and subscribing to their service. After completing the subscription, you’ll receive login credentials and can download the appropriate VPN client software for your device. Most providers offer dedicated applications for Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and Linux.
Install the VPN client software on your device and launch the application. Enter your login credentials to authenticate with the VPN service. The application will typically display a list of available server locations and connection options.
Configuration and Optimization
Once installed, you can configure your VPN settings to optimize performance and security for your specific needs. Most applications allow you to choose preferred protocols, enable security features like kill switches, and set up automatic connection preferences.
Consider configuring your VPN to start automatically when you boot your device or connect to untrusted networks. Many applications also offer split tunneling features that allow you to route only specific applications or websites through the VPN while allowing others to use your regular internet connection.
Testing and Troubleshooting
After setup, test your VPN connection to ensure it’s working properly. Verify that your IP address has changed and that DNS queries are being routed through the VPN. Various online tools can help you check for DNS leaks and confirm that your VPN is functioning correctly.
If you encounter connection issues, try different server locations or protocols. Many VPN providers offer customer support and troubleshooting guides to help resolve common problems. Keep your VPN client software updated to ensure optimal performance and security.
Frequently Asked Questions
A VPN protects your privacy by encrypting all your internet traffic and routing it through a secure server. This prevents your Internet Service Provider (ISP), government agencies, hackers, and other third parties from seeing what websites you visit, what data you transmit, or where you’re located online. The encryption makes your data unreadable to anyone who might intercept it, while the server routing masks your real IP address and location.
VPNs typically cause some speed reduction due to encryption overhead and the extra routing through VPN servers. However, high-quality VPN services minimize this impact, often reducing speeds by only 10-20%. Modern protocols like WireGuard are particularly efficient. The actual speed impact depends on factors like server distance, server load, your internet connection speed, and the VPN protocol used.
Most VPN services allow multiple simultaneous connections on different devices. The number varies by provider, typically ranging from 5-10 devices or unlimited connections. You can usually use the same VPN account on your computer, smartphone, tablet, and other devices. Some providers also offer router-level VPN setup, which protects all devices on your home network.
Free VPNs often come with significant limitations and potential security risks. Many free services have weak encryption, limited server networks, data caps, and slower speeds. More concerning, some free VPNs may log user data, inject ads, or even sell user information to third parties. For serious privacy protection, a reputable paid VPN service is recommended.
VPN usage is legal in most countries and is widely used by businesses, individuals, and even government agencies for legitimate security purposes. However, some countries with restrictive internet policies have banned or limited VPN usage. Additionally, while VPNs themselves are legal, using them to engage in illegal activities remains against the law. Always check local regulations and use VPNs responsibly.
You can verify your VPN is working by checking your IP address before and after connecting. Your IP address should change to reflect the VPN server’s location. Additionally, test for DNS leaks using online tools to ensure your DNS queries are being routed through the VPN. Most VPN applications also display connection status and server information to confirm active protection.
VPN protocols determine how data is transmitted and secured. OpenVPN offers excellent security and compatibility but can be slower. WireGuard provides superior speed and security with modern cryptography. IKEv2 is ideal for mobile devices with automatic reconnection. L2TP/IPSec offers good compatibility but slower speeds. The choice depends on your priorities for security, speed, and compatibility.
VPNs can help access geo-restricted content by making it appear as though you’re browsing from a different location. However, many streaming services actively block VPN traffic and this may violate their terms of service. Success varies by VPN provider and service. Always respect content licensing agreements and terms of service when using VPNs for streaming.
Ready to Secure Your Online Privacy?
Join millions of users who trust premium VPN protection for their digital security.
Get Started with Premium VPNConclusion
Understanding how VPNs work empowers you to make informed decisions about your online privacy and security. From the fundamental concepts of encryption and tunneling to the practical considerations of choosing and setting up a VPN service, this comprehensive guide has covered the essential aspects of virtual private network technology.
As cyber threats continue to evolve and online privacy becomes increasingly important, VPNs serve as crucial tools for protecting your digital life. Whether you’re working remotely, traveling, or simply browsing the internet at home, a quality VPN service provides the security and privacy protection you need in today’s connected world.
Remember that while VPNs are powerful privacy tools, they’re most effective when used as part of a comprehensive security strategy that includes strong passwords, updated software, and safe browsing practices. By combining these elements with a reliable VPN service, you can enjoy the internet with confidence, knowing your privacy and security are protected.
Disclosure: We may earn commission for purchases that are made by visitors on this site at no additional cost on your end. All information is for educational purposes and is not intended for financial advice. Read our affiliate disclosure.