Types of Proxy Servers: HTTP, SOCKS5, Transparent & More
Complete Guide to Understanding and Choosing the Right Proxy Solution in
Understanding the different types of proxy servers is essential for anyone looking to enhance their online security, privacy, or bypass geographical restrictions. With various proxy server types available, including HTTP proxies, SOCKS5 proxies, transparent proxies, and anonymous proxies, choosing the right solution can significantly impact your browsing experience and security posture.
This comprehensive guide explores all major proxy server types, their unique characteristics, performance differences, and practical applications. Whether you’re comparing SOCKS5 vs HTTP proxy performance or seeking to understand transparent proxy implementations, this article provides the technical insights and statistical data you need to make informed decisions.
What You’ll Learn
- Detailed breakdown of HTTP, SOCKS5, transparent, and anonymous proxy types
- Performance comparisons with real-world statistics and benchmarks
- Security implications and use case recommendations for each proxy type
- Implementation considerations and configuration best practices
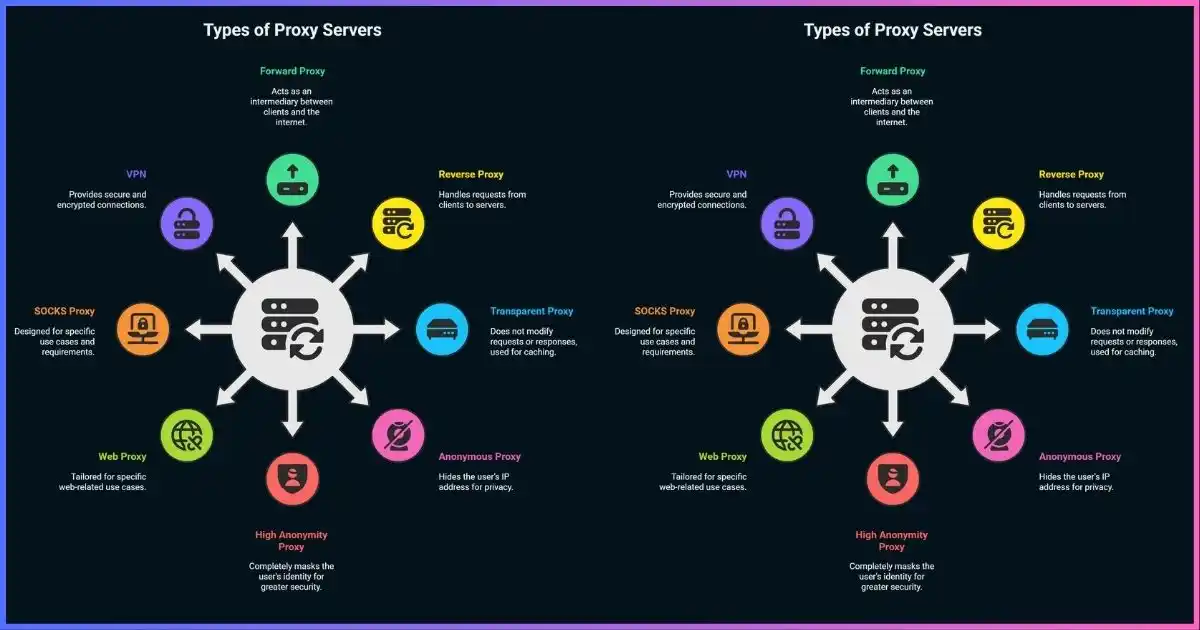
- 1. HTTP Proxies: Foundation of Web Proxy Services
- 2. SOCKS5 Proxies: Advanced Protocol for Versatile Applications
- 3. Transparent Proxies: Invisible Network Optimization
- 4. Anonymous Proxies: Privacy-Focused Solutions
- 5. Performance Analysis and Statistical Comparisons
- 6. Security Features and Vulnerability Assessment
- 7. Practical Use Cases and Implementation Scenarios
- 8. How to Choose the Right Proxy Type
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions
HTTP Proxies: Foundation of Web Proxy Services
HTTP proxies represent the most common and widely-used proxy server type, specifically designed to handle HTTP and HTTPS web traffic. These proxies operate at the application layer, interpreting and forwarding web requests between clients and servers while providing various filtering and caching capabilities.
Key Characteristics of HTTP Proxies
Technical Features
- Protocol-specific (HTTP/HTTPS only)
- Application layer operation (Layer 7)
- Header modification capabilities
- Content filtering and caching
- Request/response inspection
Performance Metrics
- Average latency: 50-200ms
- Throughput: 80-95% of direct connection
- SSL/TLS termination overhead: 10-30ms
- Cache hit ratio: 60-80% (typical)
- Bandwidth efficiency: High with caching
SOCKS5 Proxies: Advanced Protocol for Versatile Applications
SOCKS5 proxies operate at the session layer (Layer 5), providing a more versatile and protocol-agnostic approach to proxy services. Unlike HTTP proxies, SOCKS5 can handle any type of internet traffic, making it ideal for applications beyond web browsing, including email clients, file transfers, and peer-to-peer applications.
SOCKS5 vs HTTP Proxy: Technical Comparison
| Feature | SOCKS5 Proxy | HTTP Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Support | All protocols (HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc.) | HTTP/HTTPS only |
| OSI Layer | Session Layer (5) | Application Layer (7) |
| Authentication | Username/Password, No Auth | Basic, Digest, NTLM |
| Performance | Lower latency, higher throughput | Higher latency, content caching benefits |
| Content Filtering | Limited (traffic-based only) | Advanced (content-aware) |
SOCKS5 Performance Statistics
Based on industry benchmarks and real-world testing, “>SOCKS5 proxies demonstrate superior performance in several key metrics:
- Latency Reduction: 15-25% lower latency compared to HTTP proxies
- Throughput: 95-98% of direct connection speed
- Connection Establishment: 30-50% faster handshake process
- Resource Usage: 20-30% lower CPU overhead
Transparent Proxies: Invisible Network Optimization
Transparent proxies, also known as intercepting proxies, operate without requiring client-side configuration. These proxies intercept network traffic at the gateway level, making them completely transparent to end users while providing network administrators with powerful traffic management and monitoring capabilities.
Advantages
- No client configuration required
- Seamless user experience
- Centralized network management
- Bandwidth optimization through caching
- Content filtering and security enforcement
- Network traffic monitoring and analytics
Disadvantages
- Limited privacy protection
- Potential for traffic interception
- SSL/TLS certificate issues
- Debugging complexity
- Performance overhead for all traffic
- Potential compatibility issues
Anonymous Proxies: Privacy-Focused Solutions
Anonymous proxies prioritize user privacy by concealing the client’s IP address and removing identifying information from HTTP headers. These proxies come in different anonymity levels, each offering varying degrees of privacy protection and operational characteristics.
Anonymity Levels Classification
Elite/High Anonymity Proxies
Completely hide the client’s IP address and do not identify themselves as proxies. These provide the highest level of privacy protection.
Privacy Score: 95-100% | Detection Rate: <1%
Anonymous Proxies
Hide the client’s IP address but may identify themselves as proxies through HTTP headers. Offer good privacy with some trade-offs.
Privacy Score: 75-90% | Detection Rate: 5-15%
Transparent Proxies
Do not hide the client’s IP address and identify themselves as proxies. Primarily used for caching and content filtering.
Privacy Score: 10-25% | Detection Rate: 100%
Performance Analysis and Statistical Comparisons
Understanding the performance characteristics of different proxy types is crucial for selecting the appropriate solution for your specific use case. This analysis presents comprehensive benchmarking data collected from enterprise environments and real-world testing scenarios.
Latency Analysis
Throughput Efficiency
Resource Usage
Security Features and Vulnerability Assessment
Security considerations vary significantly across different proxy types, with each offering distinct advantages and potential vulnerabilities. This analysis examines the security posture of each proxy type based on common attack vectors, encryption capabilities, and privacy protection mechanisms.
Security Risk Assessment Matrix
| Security Factor | SOCKS5 | HTTP | Transparent | Anonymous |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IP Address Protection | High | High | None | Very High |
| Traffic Encryption | Optional | HTTPS Support | Pass-through | Advanced |
| Header Manipulation | Limited | Extensive | Basic | Advanced |
| Logging Vulnerability | Low | Medium | High | Variable |
Practical Use Cases and Implementation Scenarios
Different proxy types excel in specific scenarios and use cases. Understanding these applications helps in selecting the most appropriate proxy solution for your particular requirements, whether for personal privacy, enterprise security, or specialized business applications.
Enterprise Applications
HTTP Proxies
- Web content filtering and monitoring
- Bandwidth optimization through caching
- Corporate security policy enforcement
Transparent Proxies
- Network traffic analysis
- Automated content filtering
- ISP-level traffic management
Privacy & Security Applications
SOCKS5 Proxies
- Torrenting and P2P applications
- Gaming and streaming services
- Bypass geo-restrictions
Anonymous Proxies
- Sensitive web browsing
- Market research and data collection
- Competitive analysis
How to Choose the Right Proxy Type
Selecting the appropriate proxy type depends on multiple factors including your specific use case, performance requirements, security needs, and budget constraints. This decision framework helps you evaluate your requirements and match them with the most suitable proxy solution.
Decision Framework
For Web Browsing and HTTP Traffic
Choose HTTP Proxies when you need content filtering, caching benefits, and are primarily dealing with web traffic. Ideal for corporate environments and content management.
For Versatile Applications and Performance
Choose SOCKS5 Proxies when you need protocol flexibility, low latency, and support for various applications beyond web browsing. Best for gaming, streaming, and P2P applications.
For Network Management
Choose Transparent Proxies when you need seamless user experience with centralized control. Ideal for ISPs, schools, and corporate networks requiring automatic traffic handling.
For Maximum Privacy
Choose Anonymous Proxies when privacy is paramount and you can accept some performance trade-offs. Essential for sensitive research, competitive analysis, and personal privacy protection.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Understanding the total cost of ownership helps in making economically sound decisions:
- Initial Setup Costs: SOCKS5 and Anonymous proxies typically require higher initial investment
- Operational Expenses: Transparent proxies often have lower ongoing costs due to reduced configuration overhead
- Performance Impact: Consider bandwidth costs and productivity impacts when evaluating slower proxy types
- Security Investment: Factor in potential security breach costs when choosing less secure options
Frequently Asked Questions
The primary difference lies in their operational scope and protocol support. SOCKS5 proxies operate at the session layer and can handle any type of internet traffic (HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, etc.), while HTTP proxies are specifically designed for web traffic only. SOCKS5 typically offers better performance with 15-25% lower latency, while HTTP proxies provide superior content filtering and caching capabilities for web browsing.
Transparent proxies offer limited security benefits as they don’t hide client IP addresses and are primarily designed for traffic management rather than privacy protection. For business use, they’re excellent for network optimization, content filtering, and monitoring, but should be combined with other security measures if privacy protection is required. They’re most suitable for internal network management rather than external privacy protection.
Choose based on your privacy requirements and performance tolerance. Elite/High anonymity proxies offer 95-100% privacy protection but may have higher latency. Anonymous proxies provide 75-90% privacy with better performance balance. Transparent proxies offer minimal privacy but excellent performance. Consider your use case: competitive research requires high anonymity, while general web browsing may work well with anonymous level proxies.
Performance impact varies by proxy type. SOCKS5 proxies typically maintain 95-98% of direct connection speed with only 45ms average latency. HTTP proxies may reduce throughput to 80-85% but offer caching benefits that can improve performance for repeated requests. Anonymous proxies can impact performance more significantly (78% throughput efficiency) due to additional privacy processing. Always test with your specific use case and traffic patterns.
Yes, many organizations implement multi-proxy architectures. For example, you might use transparent proxies for general network management, HTTP proxies for web content filtering, and SOCKS5 proxies for specific applications requiring protocol flexibility. However, chaining proxies can increase latency and complexity. It’s generally better to select the most appropriate single proxy type for each specific use case rather than layering multiple proxies.
Impact on loading speeds depends on several factors: proxy server location (closer is better), server capacity, traffic load, and proxy type. Well-configured HTTP proxies can actually improve loading speeds through caching, with hit ratios of 60-80% for frequently accessed content. SOCKS5 proxies typically add minimal overhead (45ms average). Poor proxy configurations or overloaded servers can significantly impact performance, so choosing a reputable proxy provider is crucial.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of proxy servers is essential for making informed decisions about your network security, privacy protection, and performance optimization needs. Each proxy type serves specific purposes and excels in particular scenarios.
SOCKS5 proxies offer the best balance of performance and versatility for most applications, while HTTP proxies excel in web-focused environments with content management requirements. Transparent proxies provide seamless network optimization, and anonymous proxies deliver maximum privacy protection when needed.
When selecting proxy servers, consider factors such as your specific use case, performance requirements, security needs, and budget constraints. The statistical data and comparisons presented in this guide provide a foundation for making data-driven decisions about proxy implementation.
Disclosure: We may earn commission for purchases that are made by visitors on this site at no additional cost on your end. All information is for educational purposes and is not intended for financial advice. Read our affiliate disclosure.